Kamis, 15 November 2012
Basics of Wireless Networks
Basics of Wireless Networks
SUMMARY
The first commercially available radio and telephone system, known as the improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS), was put into service in 1946. This system was quite unsophisticated , as there were no solid-state electronic available at the time. Given these constrictions, the number of channels available did not come close to satisfying the demand.
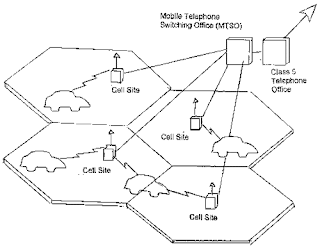
The solution to this problem was cellular radio. This system divided metropolitan area into several cells, and each cells operating on a set frequencies that differed from another cells. Two important characteristic of cellular systems contribute to their usefulness. The first is their controlled handoff. Second, systems were designed to locate particular subscribers by paging them in each of the cells. The initial transmission technology used between the vehicle and thecell site was analog in nature and known as AMPS (advanced Mobile Phones System). In Europe GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and TDMA (time-division multiple access) now known as Global System for Mobile Communications.
Develop spread-spectrum technology CDMA (called code-division multiple access). The continuing growth of cellular communications led government and government in US to search for additional way to satisfying customer. This search led to the development of the PCS (personal communications service) industry. Additional frequency band were allocated for their use and rather than assign them to the first comer. Unfortunately, after acquiring the spectrum, many of the new potential operators went bankrupt and never actually had a chance to use it. In Canada, the decision was based on a beauty contest, a comparison of business cases, technology, and future plans, rather than the bidding process.
ABSTRACT
The first commercially available radio and telephone system, known as IMTS (Improved Mobile Telephone Service) was less sophisticated. Then, introduced cellular radio, this system divided metropolitan area into several cells, and each cells operating on a set frequencies. Two important characteristic of cellular systems contribute to their usefulness. The first is their controlled handoff. Second, systems were designed to locate particular subscribers by paging them in each of the cells. Digital transmission was later developed was TDMA ( time-division multiple access). This selected known as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications). Then, the developed spread-spectrum technology called CDMA (code-division multiple access). The developed search was personal communications service (PSC) industry.